EU's AI Act Explained: Key Takeaways for Website Owners

What is the European AI Act?
The European AI Act is a set of regulations introduced by the European Union to ensure the safe and ethical use of artificial intelligence. Its primary goal is to protect users while promoting innovation and competition within the AI industry. The regulations will be monitored by authorities in each country as well as an EU commission.
Information source: AI Act | Shaping Europe’s digital future (europa.eu)
Key points European AI Act
Risk classes determine AI regulation
AI systems are classified into four risk categories: unacceptable, high, limited, and minimal.
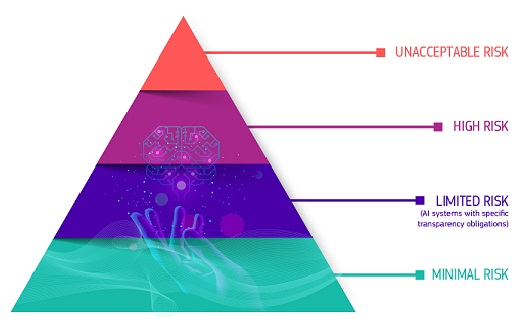
Examples of AI applications for each class
Unacceptable Risk AI
- Social Scoring Systems by Governments: AI systems used to rank citizens based on behaviour, socio-economic status, or personal characteristics.
- Real-Time Biometric Identification in Public Spaces: Systems that scan and identify individuals in real-time for surveillance purposes without their consent.
Those groups of AI systems are banned in the future!
High-Risk AI
- Biometric Identification and Categorization of Natural Persons: AI used for facial recognition or fingerprint scanning for access control in workplaces or secure facilities.
- Healthcare AI: Diagnostic tools and systems used in medical devices or for recommending treatments.
This group of AI systems, which might impact safety or fundamental rights, must meet strict requirements and will be regularly monitored for compliance. Users must be made aware when they are interacting with this type of AI.
Limited Risk AI
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: AI systems that interact with users on websites to provide customer service or support.
- Recommendation Systems: AI that suggests products, services, or content to users based on their past behaviour (e.g. online shopping recommendations, movie or music suggestions).
Limited and minimal risk AI systems face fewer regulatory obligations.
Minimal Risk AI
- Spam Filters: AI used to detect and filter out unwanted email.
- AI-Powered Autocorrect and Grammar Checkers: Tools that assist users in writing by suggesting corrections and improvements.
What does the EU AI regulation say about large language models like GPT-4o, Gemini and Llama3?
In future, anyone who develops such basic models must provide information about the training data and test procedures by means of "technical documentation". Proof must also be provided that applicable copyright law has been complied with. For users who are using these tools, there are no restrictions at the moment.
When will the new AI Act be in effect?
The EU wants to introduce the new regulations gradually. For example, bans will not apply until February 2025 and some regulations for high-risk AI systems will not apply until 36 months after the start of the AI Act.
Tips for using AI on your website and content-creation
As the AI Act is mainly targeting companies who develop AI applications there is only a limited need for immediate action. However, there are some recommendations for website administrators.
- User Awareness: You must inform users when content or images are generated by AI. This can be done through clear labels or disclaimers.
- Clear Communication: Ensure users understand how AI-generated content is created and used on your website.
- Quality Control: Regularly review AI-generated content to prevent the dissemination of harmful, misleading, or inappropriate information.
- Compliance with GDPR: Ensure that AI tools you are using adhere to the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), safeguarding user data.
Disclaimer: This content was partially created with the help of ChatGPT based on the GPT-4 architecture.
Latest news
Offentlig sektor flyter over av kunnskap – fra utredninger til evalueringer. Utfordringen har lenge vært å finne denne informasjonen i havet av PDF-er. Ramsalt har vært sentral i utviklingen av Kudos – en nasjonal kunnskapsportal. Ved å implementere banebrytende KI-basert dokumentanalyse, har vi bidratt til å snu en kaotisk dokumentbase til en gullgruve av søkbar innsikt.

Ramsalt’s Client Resource Manager, Nina Holzapfel, will speak at DrupalCon 2025 about how to manage scope creep and keep projects on track. With years of experience leading Drupal projects and keeping clients happy, she shares practical insights for teams who want smoother delivery and stronger results. In this interview, Nina explains why this topic matters and what attendees can expect from her session.

DrupalCon Vienna 2025 is almost here. Ramsalt Labs is ready to join the global Drupal community to share insights, contribute, and connect. This event is a chance for us to strengthen Drupal, learn from peers, and meet face to face with clients, partners, and colleagues.

Ramsalt Lab, one of Northern Europe’s leading web development agencies, is pleased to announce a new phase of growth with strategic changes to its leadership team.




